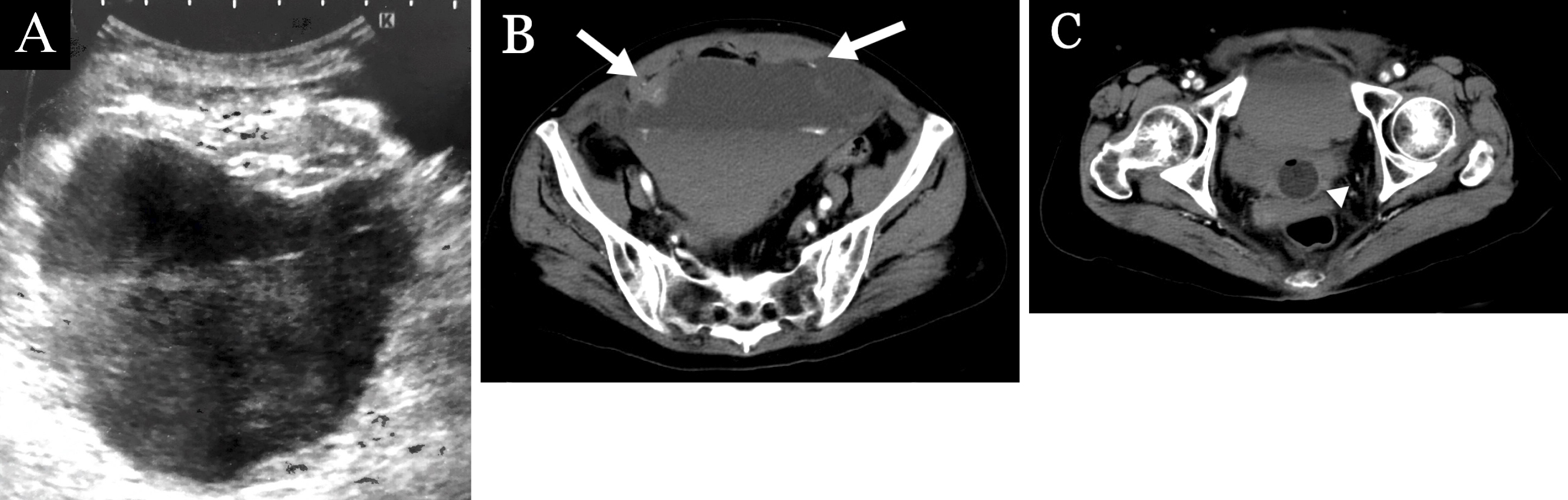
Figure 1. a. An ultrasound image resembling urinary bladder hematoma. b. Dynamic contrast-enhanced computed tomography (DCE-CT) showing a large hematoma in the rectus sheath, which extended below the arcuate line, with active bleeding and the hematocrit effect. There was evidence of contrast agent leakage between the rectus abdominis muscle and the hematoma. (arrows) c. A DCE-CT showing the hematoma compressing the urinary bladder, which contains a Foley catheter (arrowhead) (“pseudobladder sign”).
From: Giant Rectus Sheath Hematoma: Pseudobladder Sign