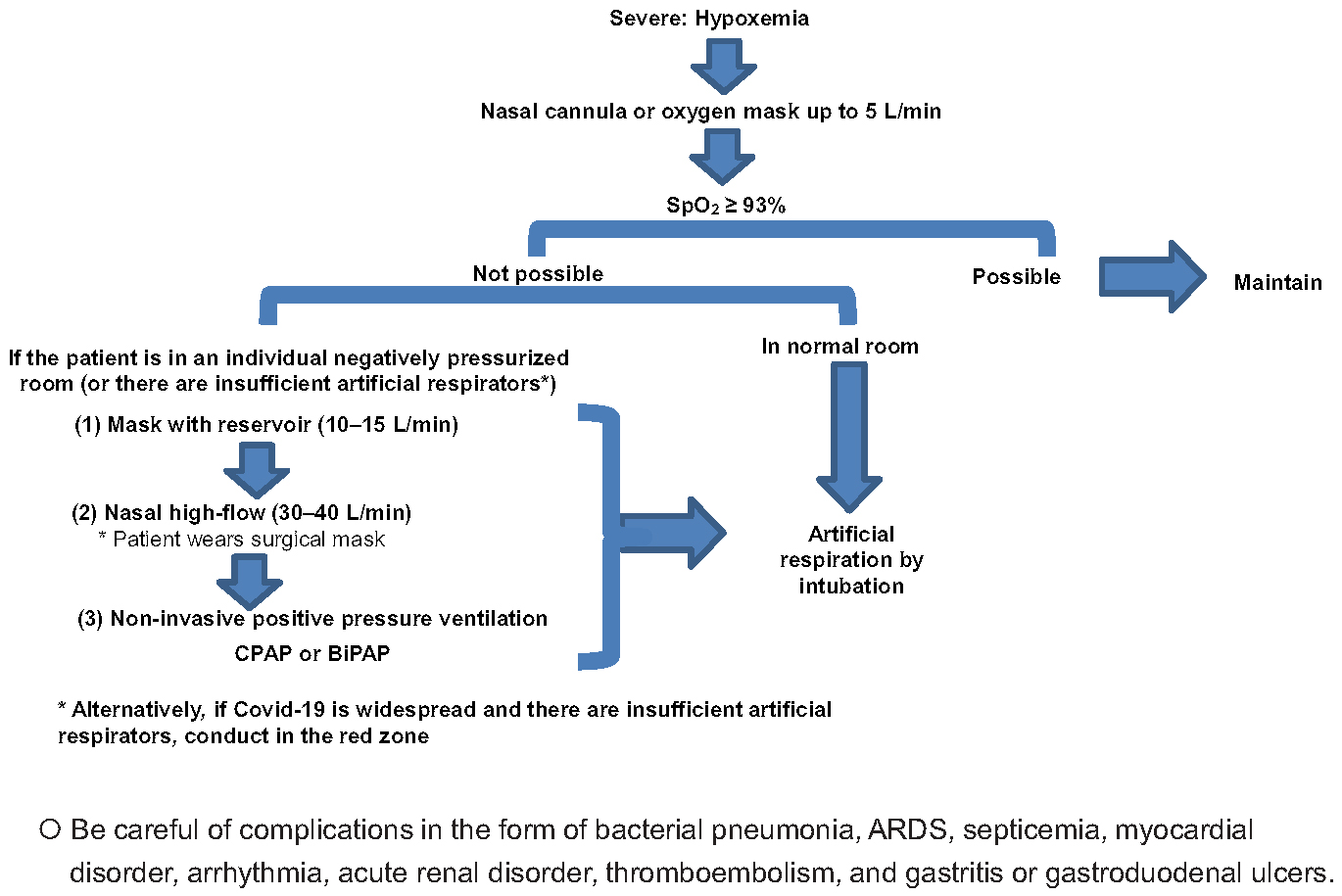
Figure 1. A clinical flowchart to select respiratory support modalities for COVID-19 cases. Ordinarily, SpO2 ≥ 93% should be maintained by a nasal cannula up to O2 5 L/min or an oxygen mask up to O2 10 L/min.
*Note: When a nasal cannula is used, the patient should wear a surgical mask to suppress aerosol generation.
Consider intubation if SpO2 ≥ 93% cannot be maintained even with O2 administration by means of an oxygen mask. In addition, intubation or artificial respiration management should ideally be performed earlier than usual.
*Note: Masks with a reservoir (10-15 L/min), nasal high-flow, and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation are normally considered at this stage, but there is a risk of nosocomial infection due to aerosol generation so the use of individual negatively pressurized rooms is desirable. Confirm that the flow is between 30 and 40 L/min when using high-flow and that the cannula is within the nasal cavity. In addition, have the patient wear a surgical mask to suppress aerosol generation.
From: Case Management of COVID-19 (Secondary Version)