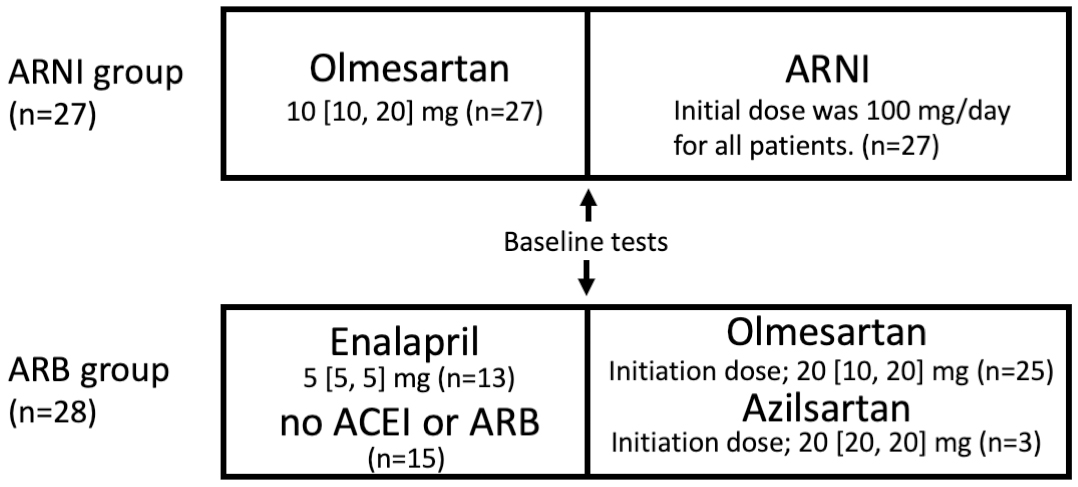
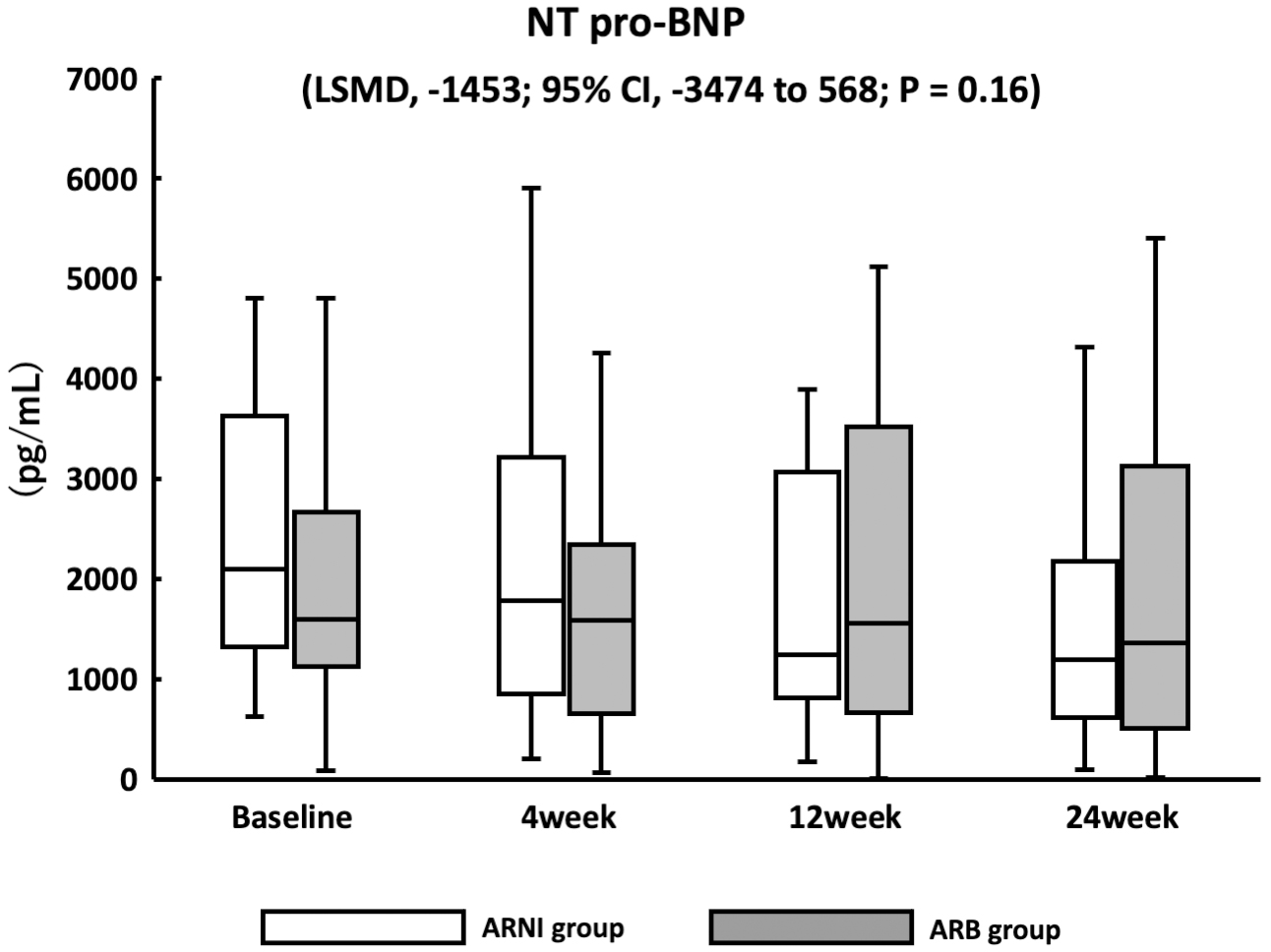
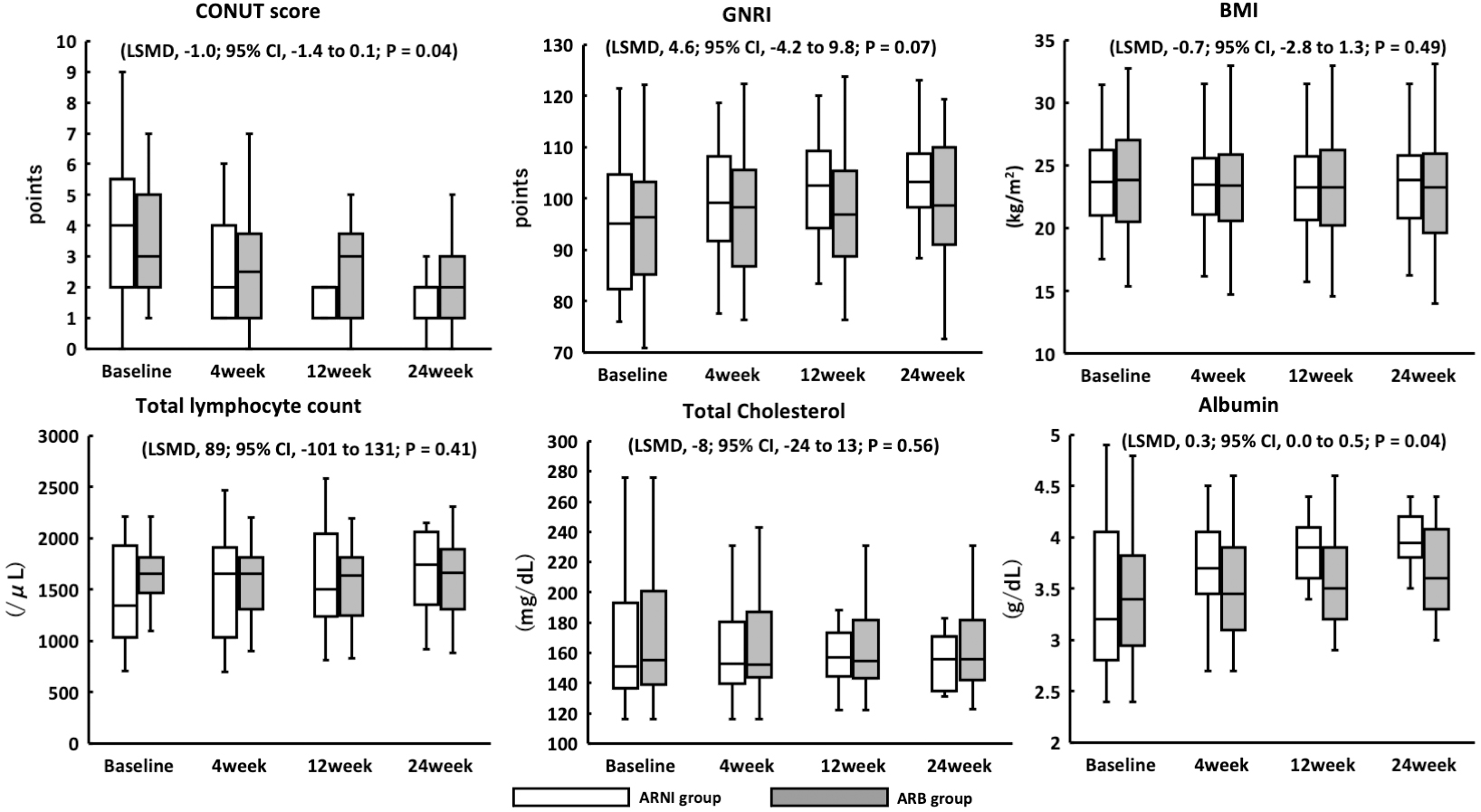
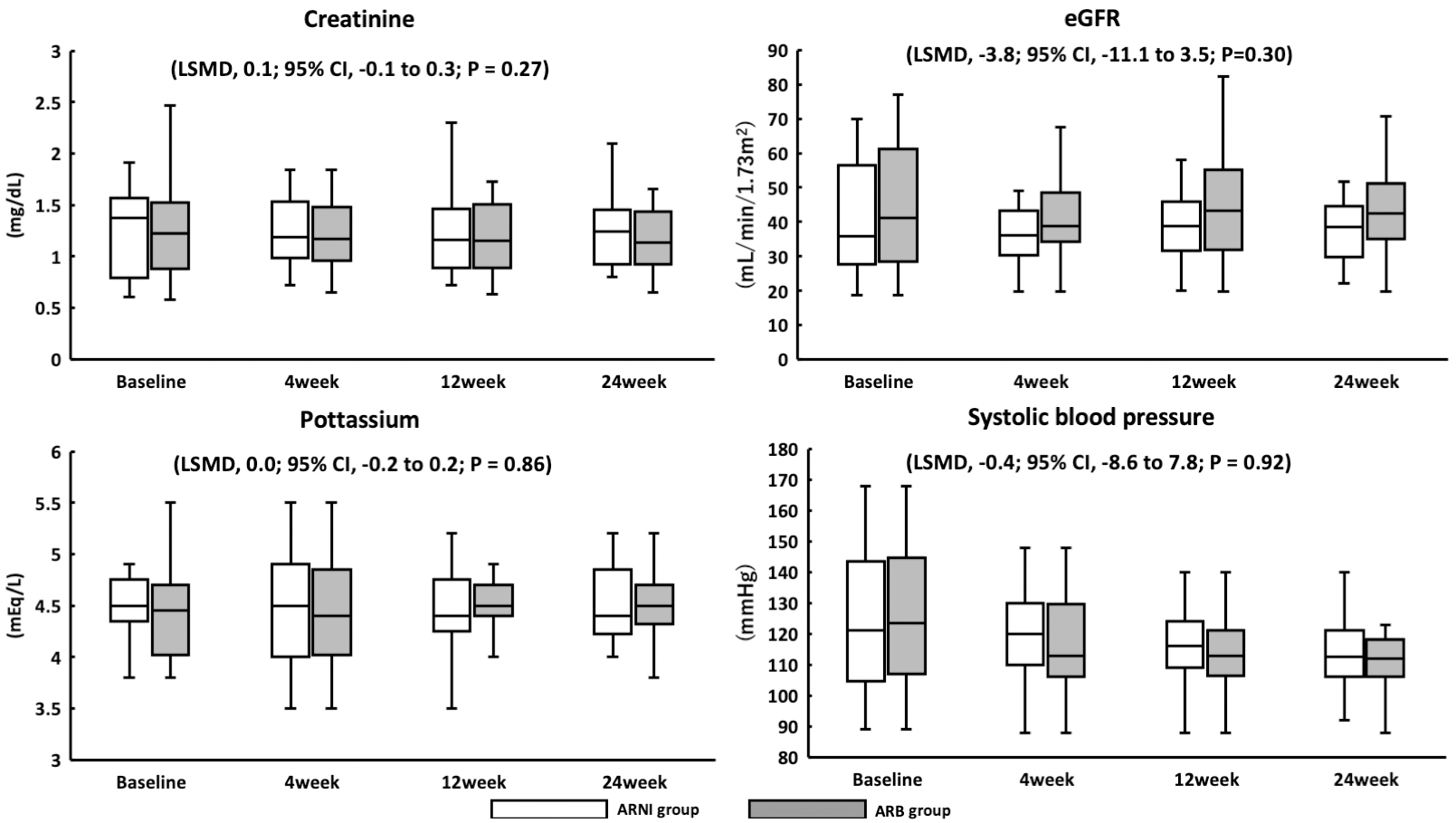
Figure 1. Study scheme.
The ARNI and ARB groups enrolled 27 and 28 patients, respectively. In the ARNI group, all patients had been treated with olmesartan prior to ARNI therapy. The initial ARNI dose was 100 mg for all patients and titrated according to blood pressure. In the ARB group, 13 patients used enalapril and 15 patients did not use ACEI or ARB prior to ARB therapy. Olmesartan and azilsartan were used in 25 and 3 patients, respectively. Both olmesartan and azilsartan had a median dose of 20 mg at initiation, and the dose was increased according to blood pressure.
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; ARNI, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor.
From: Real-world Practical Experience of Angiotensin Receptor-neprilysin Inhibitor in Older Japanese Patients with Chronic Heart Failure