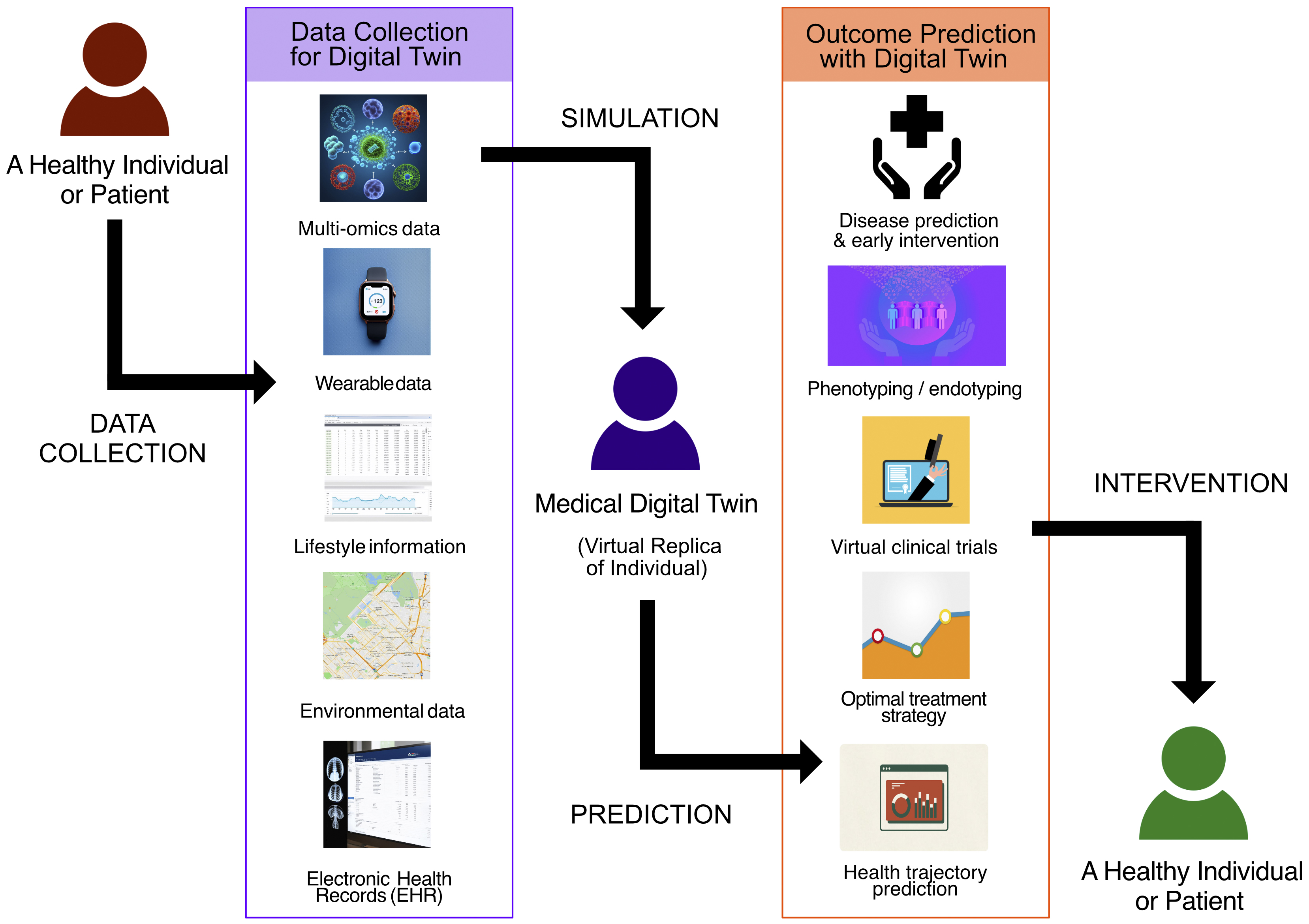
Figure 1. Multi-omics representation of homeostatic disruption in multifactorial diseases
The stages of homeostatic disruption in multifactorial diseases have been shown through the integration of multi-omics data. Multi-omics layers show the transition from a healthy state, characterized by stable and balanced omics layers (epigenome, genome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and microbiome), to a predisease state, where slight disruptions and interactions between layers appear, and finally to a disease state, marked by significant disruptions and altered interactions. This process emphasizes how multi-omics data can represent the continuum from health to disease onset.
From: The Era of Preemptive Medicine: Developing Medical Digital Twins through Omics, IoT, and AI Integration
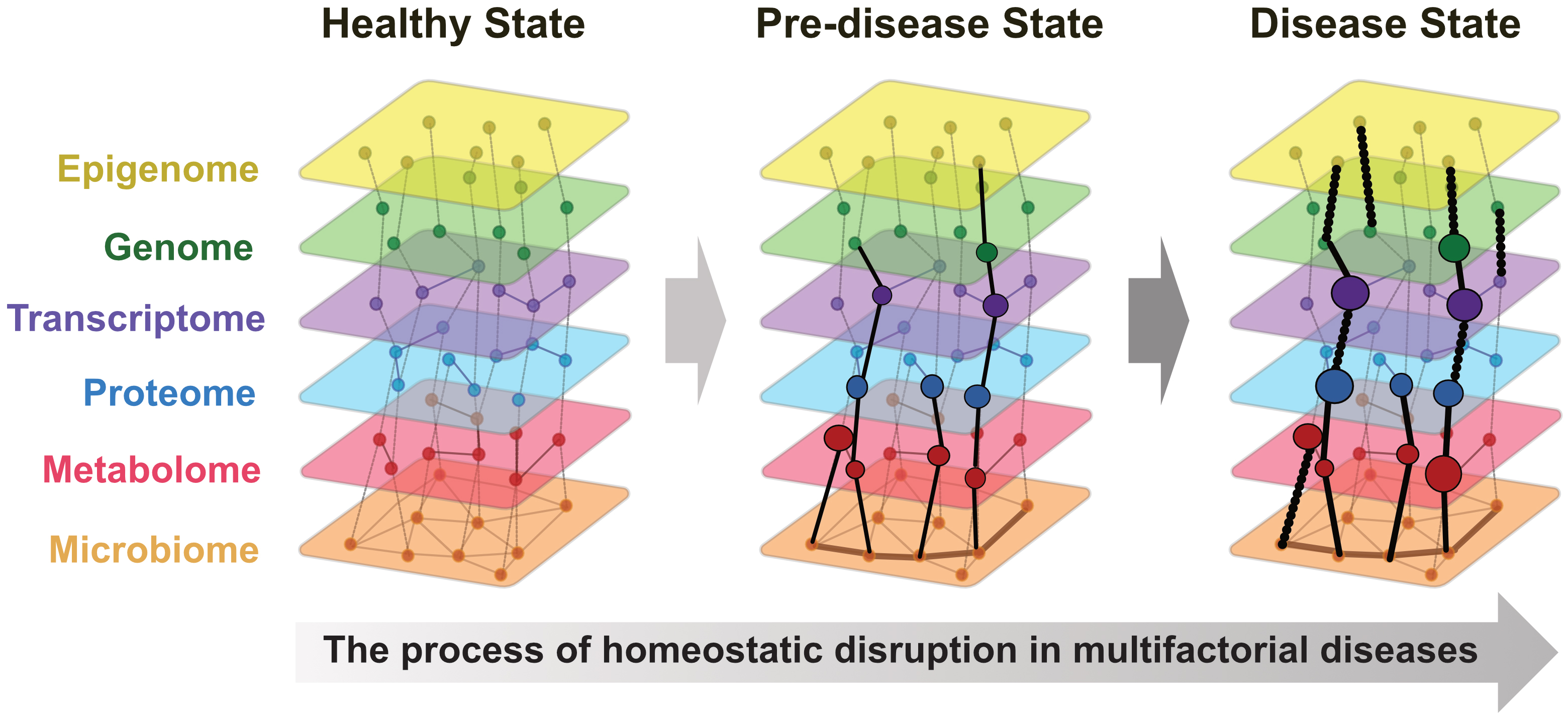
Figure 2. Creation and application of a medical digital twin
Data such as multi-omics data, wearable data, lifestyle information, environmental data, and electronic health records are collected from a healthy individual or patient. These data are used to create a medical digital twin, which serves as a virtual replica of the individual and enables various outcome predictions. The predictions include disease prediction and early intervention, phenotyping/endotyping, virtual clinical trials, optimal treatment strategies, and health trajectory prediction. The resulting insights can guide personalized interventions for the individual.
From: The Era of Preemptive Medicine: Developing Medical Digital Twins through Omics, IoT, and AI Integration