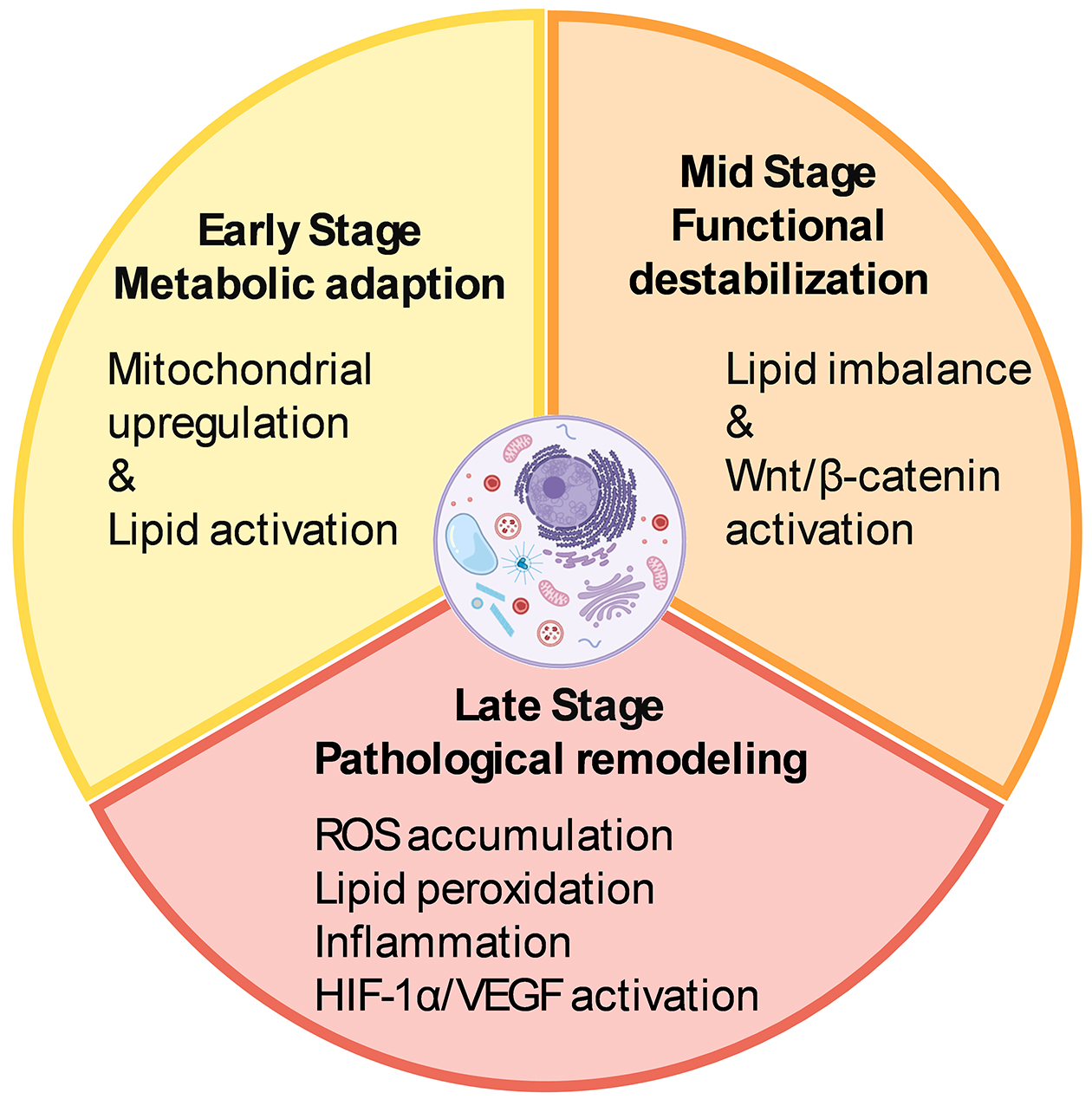
Figure 1. Effects of visual conditions and ON/OFF pathway alterations on axial elongation. This schematic illustrates how visual and genetic factors disrupt ON/OFF signaling and promote axial elongation. Hyperopic defocus impairs ON pathway signaling and disrupts feedback control of axial growth. Nyx and Lrit3 mutations impair ON signaling and increase myopia susceptibility. Mesopic light sustains rod-driven ON input, while high contrast enhances OFF activation. These changes disrupt emmetropization feedback and drive ocular elongation.
PR: Photoreceptor; OS: outer segment; IS: inner segment; ONL: outer nuclear layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; IPL: inner plexiform layer; GCL: ganglion cell layer; CBC: cone bipolar cell; RB: rod bipolar cell.
From: Mechanisms Underlying Myopia Progression from Visual Signaling to Metabolic Remodeling in Retina
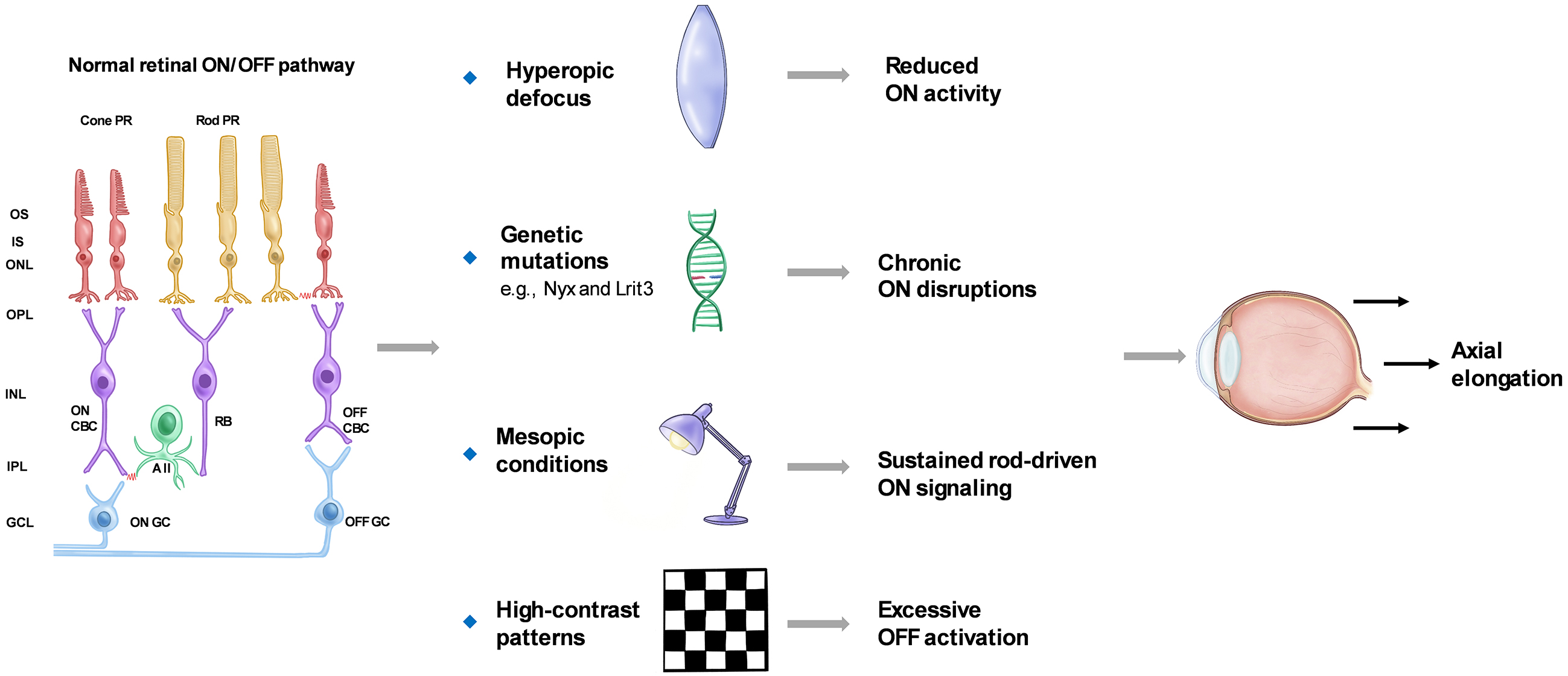
Figure 2. Temporal progression of metabolic remodeling in the myopic retina.
The early stage features mitochondrial upregulation and lipid metabolism activation as adaptive responses. Mid-phase destabilization involves lipid imbalance and aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In the late stage, pathological remodeling is marked by oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, chronic inflammation, and HIF-1α/VEGF pathway activation, creating a microenvironment prone to degeneration. The illustrations were created using BioRender (www.biorender.com).
HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.
From: Mechanisms Underlying Myopia Progression from Visual Signaling to Metabolic Remodeling in Retina