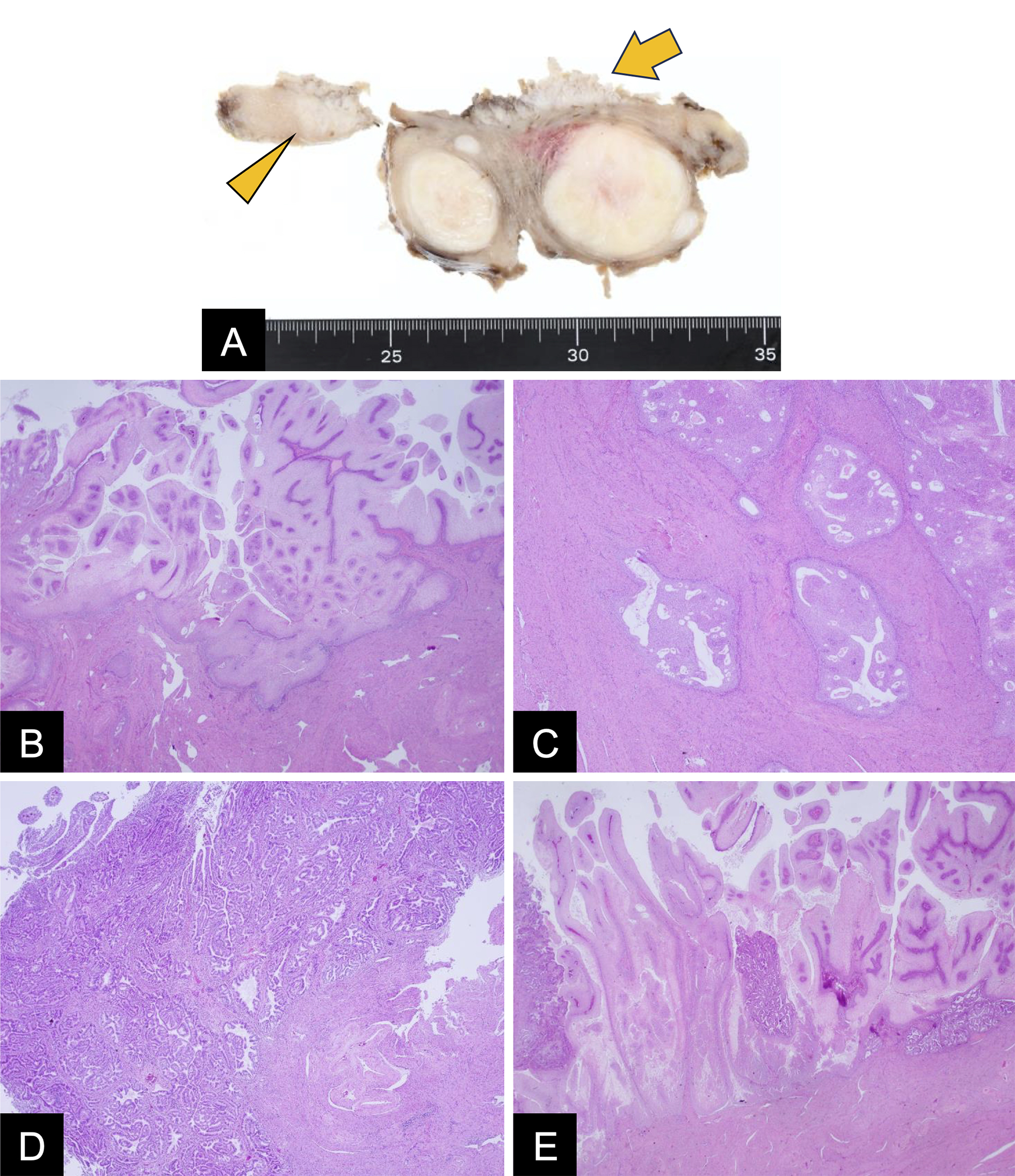
Figure 1. MRI findings of endometrial lesion.
The lesion shows low signal intensity on the T2-weighted image compared to normal endometrium (A, B). There were no findings suggestive of adenomyosis. On contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image, the lesion demonstrates weak enhancement with suspected invasion into the posterior wall of the uterine corpus (C; arrow). While the lesion shows high signal intensity on DWI (D), the ADC value of 0.96 × 10-3 mm2/sec indicates no substantial diffusion restriction (E; dotted circle). Multiple uterine leiomyomas were observed.
ADC: apparent diffusion coefficient; DWI: diffusion-weighted imaging; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.
From: Ichthyosis Uteri Mimicking Endometrial Cancer with Apparent Myometrial Invasion
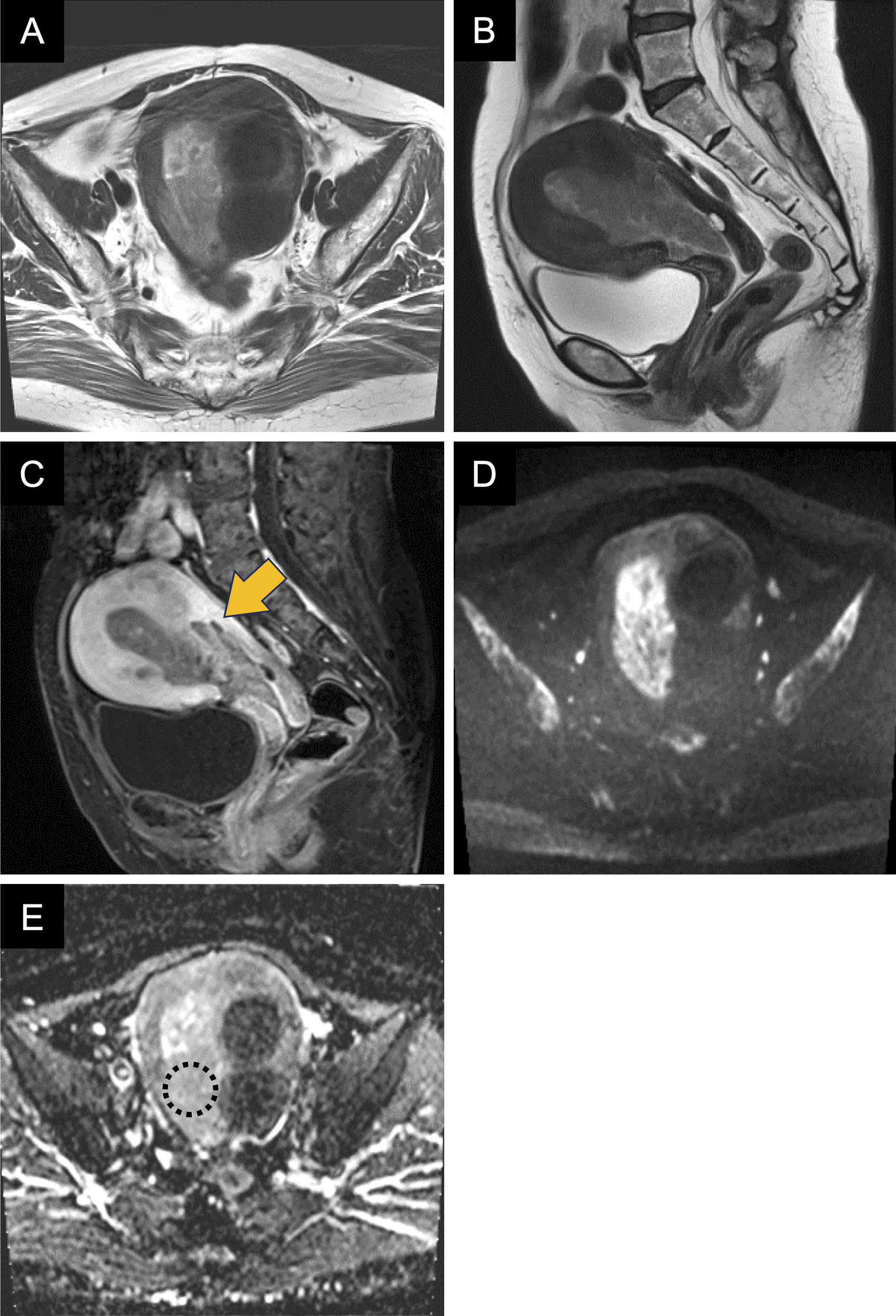
Figure 2. Gross and microscopic pathology findings.
Gross examination revealed a white papillary lesion on the endometrial surface (A; arrow) with focal myometrial extension (A; arrowhead). Microscopically, extensive papillary proliferation of bland squamous epithelium was observed (B), which extended 15 mm along adenomyosis (C). Residual glands showed hyperplasia (D), with areas showing mixed squamous metaplasia and hyperplastic changes (E).
From: Ichthyosis Uteri Mimicking Endometrial Cancer with Apparent Myometrial Invasion