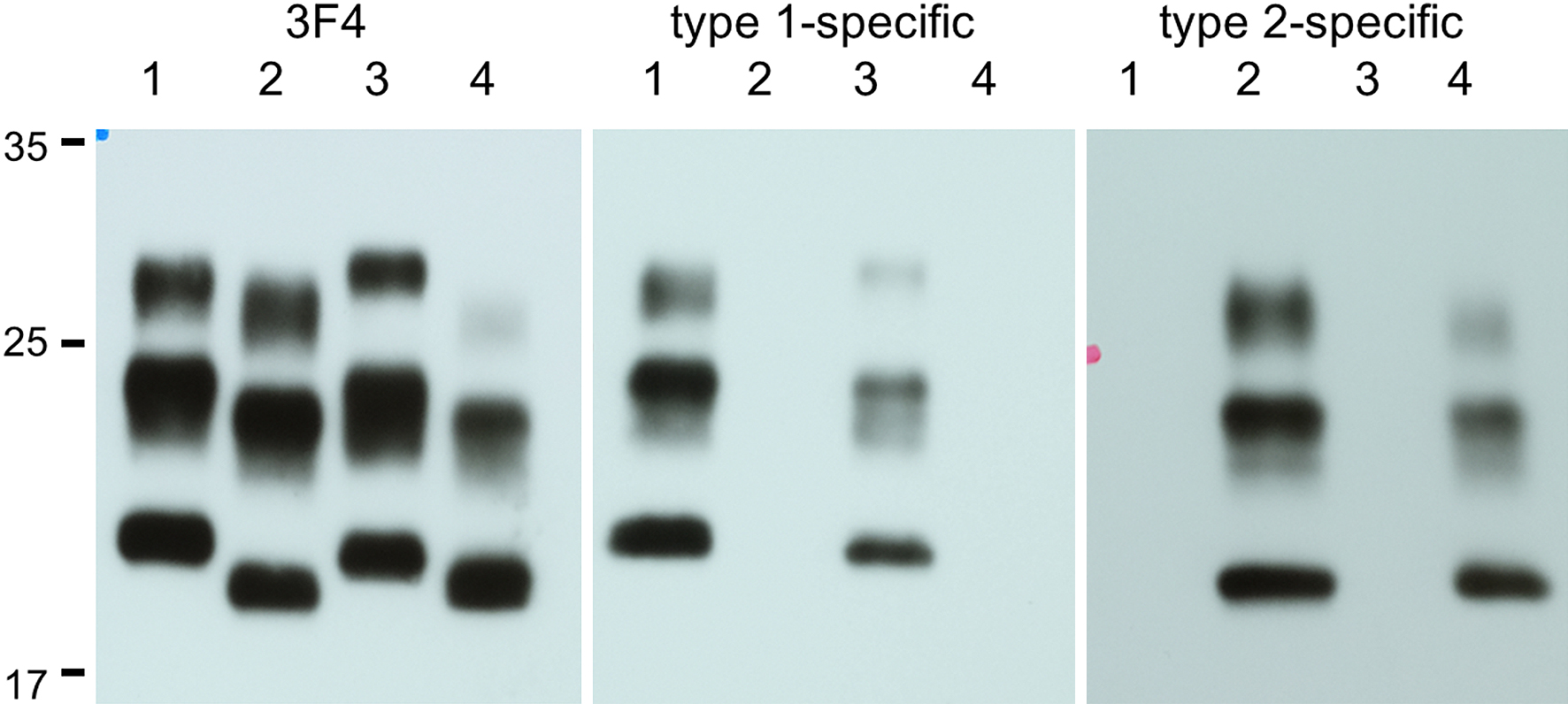
Figure 1. Neuroimaging of the present case.
A. Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) obtained on April 2013. Mild hyperintense lesions in the parietal and posterior lobes.
B. T1-weighted image obtained on June 2013. Mild cerebral atrophy is present. DWI was not performed at the same time.
C, D. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) obtained on December 2013. DWI (C) shows hyperintense lesions in cortical ribbons and caudate nuclei. No apparent signal abnormalities are present in fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images (D).
E. 99mTc-ECD SPECT combined with the easy Z-score imaging system (eZIS) (July 2013) shows hypoperfusion at the level of the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes, including the precuneus and posterior cingulate gyrus.
From: Importance of Neuropathological Diagnosis of Dementia Patients in Family Practice
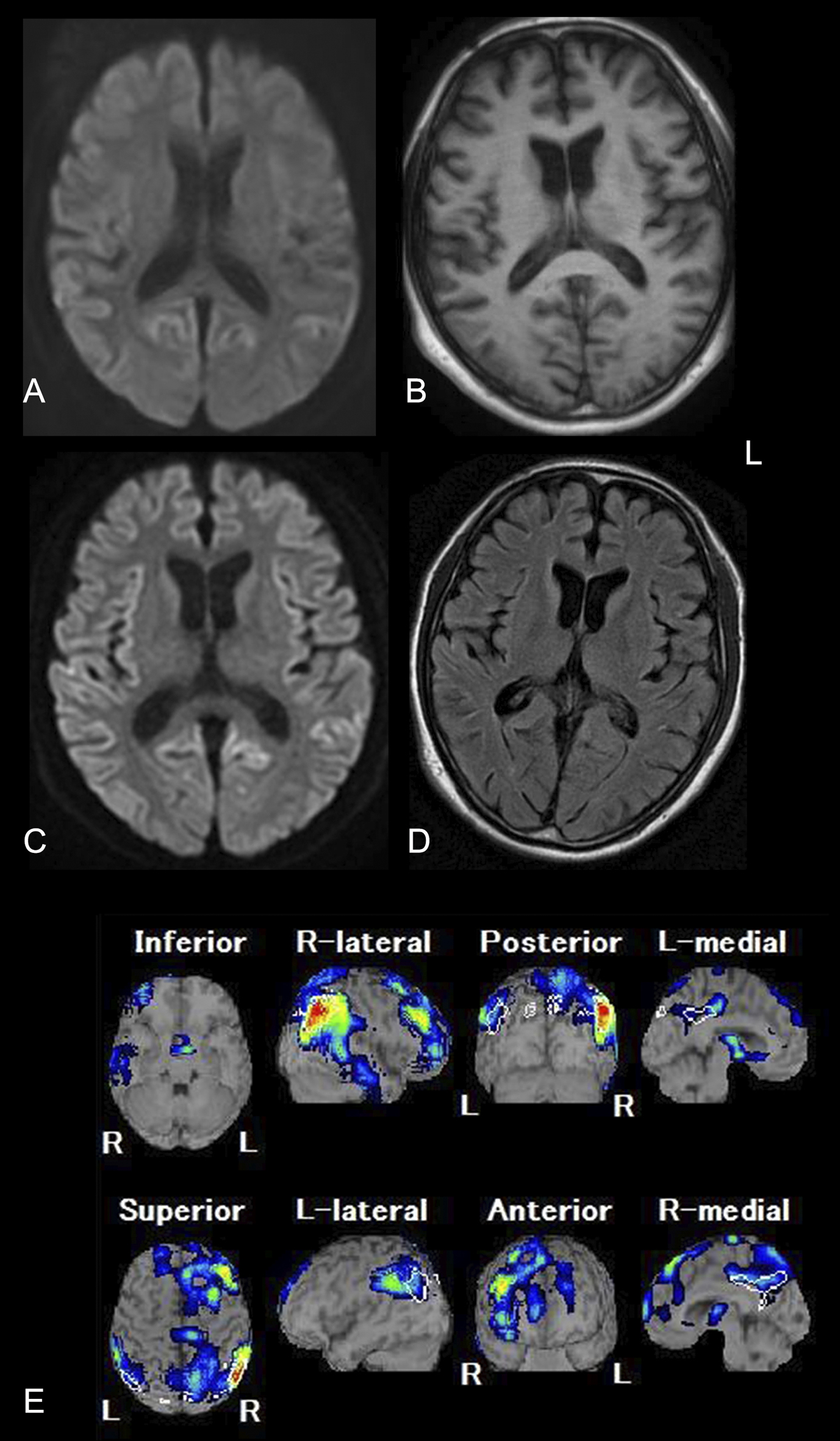
Figure 2. Neuropathological findings of the present case.
A. Diffuse cerebral atrophy of the cerebral hemisphere after formalin fixation. Bar = 1cm.
B. Large vacuolar changes are present in the temporal cortex. Hematoxylin and eosin staining. Bar =50μm.
C. Coarse 3F4 immunoreactive deposits are seen in the temporal cortex. Immunohistochemistry using an antibody (3F4) raised against prion protein. Bar =50μm.
D. Occasional dense 3F4 immunoreactive deposits in the cerebellar cortex are negative for thioflavin-S staining. Synaptic pattern 3F4 immunoreactivity was also present in the cerebellar cortex. Immunohistochemistry using an antibody (3F4) raised against prion protein. Bar =50μm.
From: Importance of Neuropathological Diagnosis of Dementia Patients in Family Practice
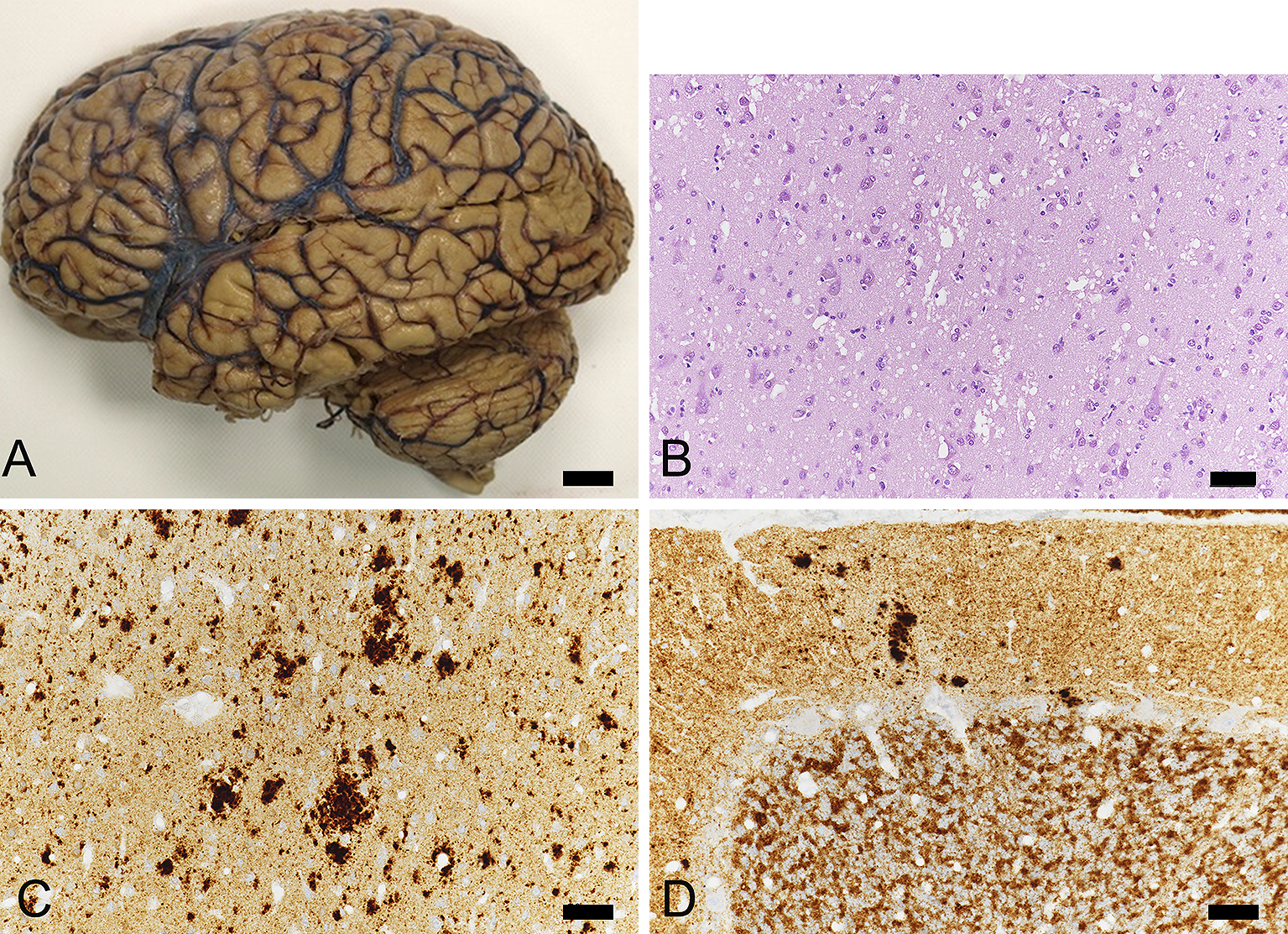
Figure 3. Western blot analysis of the patient.
Western blot patterns of PrPSc from the frontal (Lane 2) and cerebellar (Lane 3) show type 2 and type 1, respectively. The results are also confirmed using specific antibodies for type 1 and type2 PrP. Lane 1: MM1 control, Lane 2: frontal cortex of the case, Lane 3: the cerebellar cortex from the case, Lane 4: MM2 control. Left side, molecular weight marker (kilodaltons)
From: Importance of Neuropathological Diagnosis of Dementia Patients in Family Practice