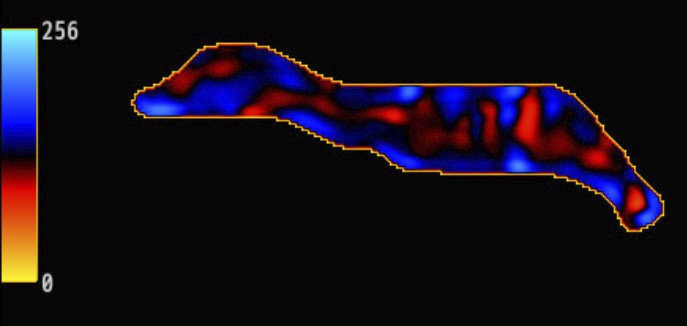
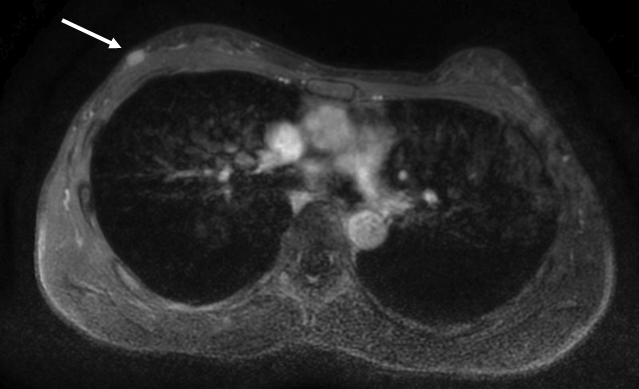
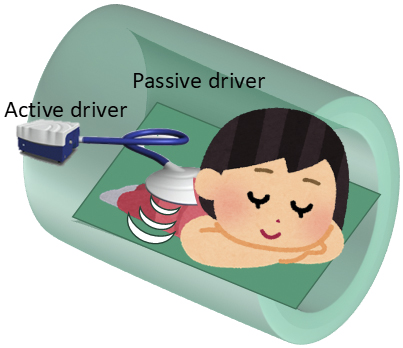
Figure 2. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) demonstrated that the mass was notably stiffer than the mammary gland (Figure 2). Areas marked with a crosshatch symbol (X) indicate regions unsuitable for stiffness measurement. Stiffness maps matching the anatomical structure of the contralateral breast were obtained, and waves propagated without interference in the MRE wave images (Figure 3). The breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was obtained using a 3.0-T MRI system (Signa™ Pioneer; GE HealthCare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). Breast MRE imaging parameters are set as follows: a 16-channel breast coil, repetition time = 1000 ms, echo time = 59.2 ms, motion encoding gradient frequency = 80 Hz, vibration frequencies = 60 Hz, vibration stimulation = 70%, temporal phases = 4, number of excitations = 2, field of view = 380 mm, acquisition matrix = 64 × 64, slice thickness = 8 mm, number of slices = 13, pixel size = 5.9 × 5.9 × 8 mm3, and acquisition times of 69 s.
From: Detecting Breast Cancer via Innovative Magnetic Resonance Elastography with External Vibrations to the Back
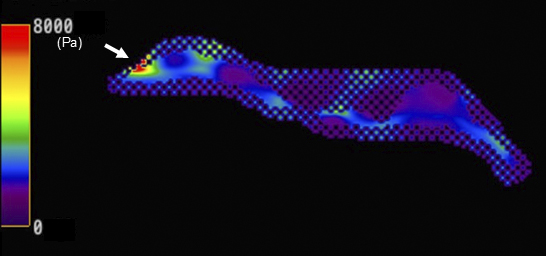
Figure 3. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) demonstrated that the mass was notably stiffer than the mammary gland (Figure 2). Areas marked with a crosshatch symbol (X) indicate regions unsuitable for stiffness measurement. Stiffness maps matching the anatomical structure of the contralateral breast were obtained, and waves propagated without interference in the MRE wave images (Figure 3). The breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was obtained using a 3.0-T MRI system (Signa™ Pioneer; GE HealthCare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). Breast MRE imaging parameters are set as follows: a 16-channel breast coil, repetition time = 1000 ms, echo time = 59.2 ms, motion encoding gradient frequency = 80 Hz, vibration frequencies = 60 Hz, vibration stimulation = 70%, temporal phases = 4, number of excitations = 2, field of view = 380 mm, acquisition matrix = 64 × 64, slice thickness = 8 mm, number of slices = 13, pixel size = 5.9 × 5.9 × 8 mm3, and acquisition times of 69 s.
From: Detecting Breast Cancer via Innovative Magnetic Resonance Elastography with External Vibrations to the Back