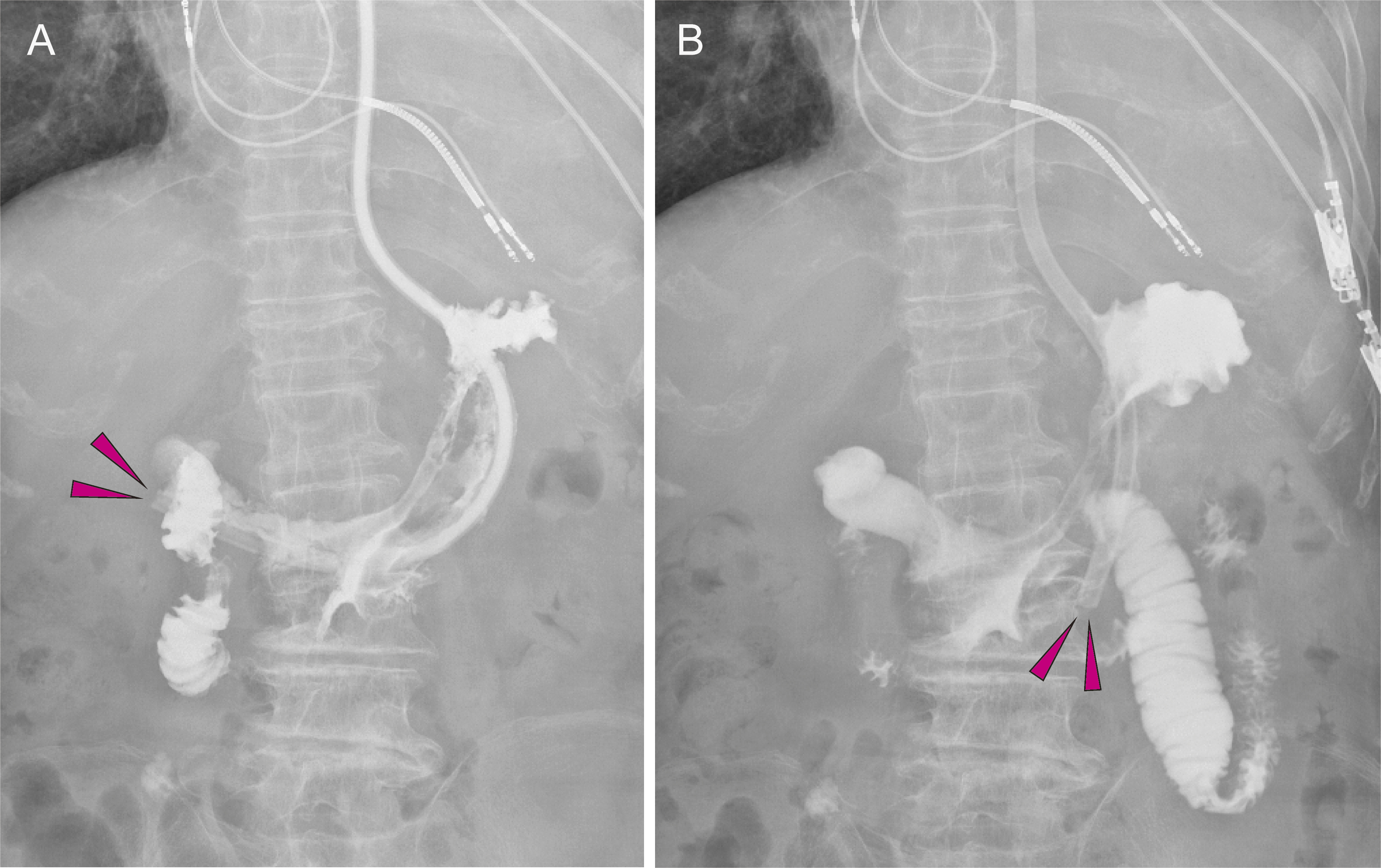
Figure 1. Echocardiography of the patient.
The patient exhibited asymmetric septal hypertrophy; the interventricular septum measuring 16 mm and the left ventricular posterior wall measuring 9.1 mm (left and middle panel). Additionally, increased blood flow through the left ventricular outflow tract confirmed the diagnosis of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (right panel).
From: Hypotensive Dumping Syndrome in Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
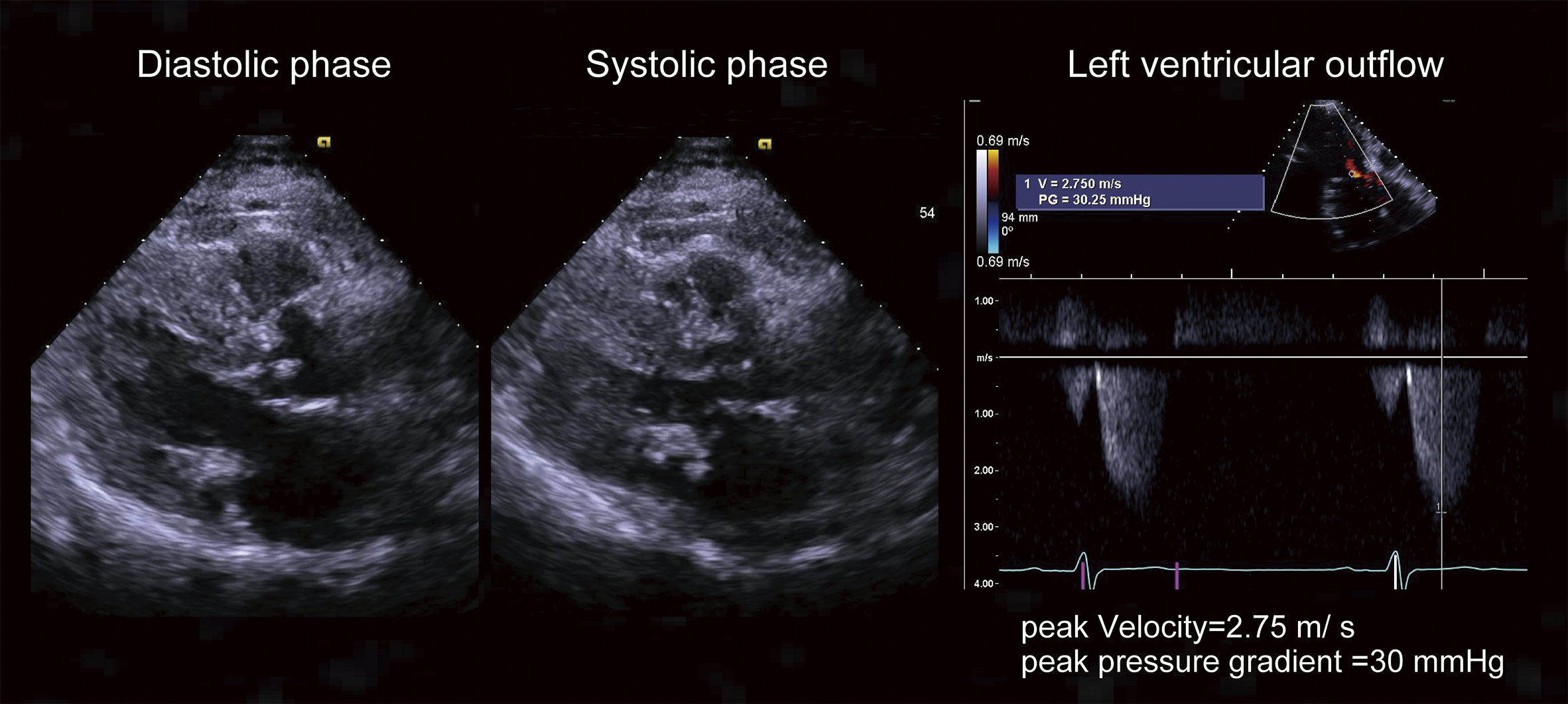
Figure 2. Radiography at the admission.
A: Chest radiography revealed lung consolidation. Note that the patient is endotracheally intubated and a nasogastric tube is inserted.
B: Abdominal radiography. The nasogastric tube tip was beyond the diaphragm, and the tube was fixed at the nasal cavity at 65 cm. Note: the height of the patient is 153 cm.
From: Hypotensive Dumping Syndrome in Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
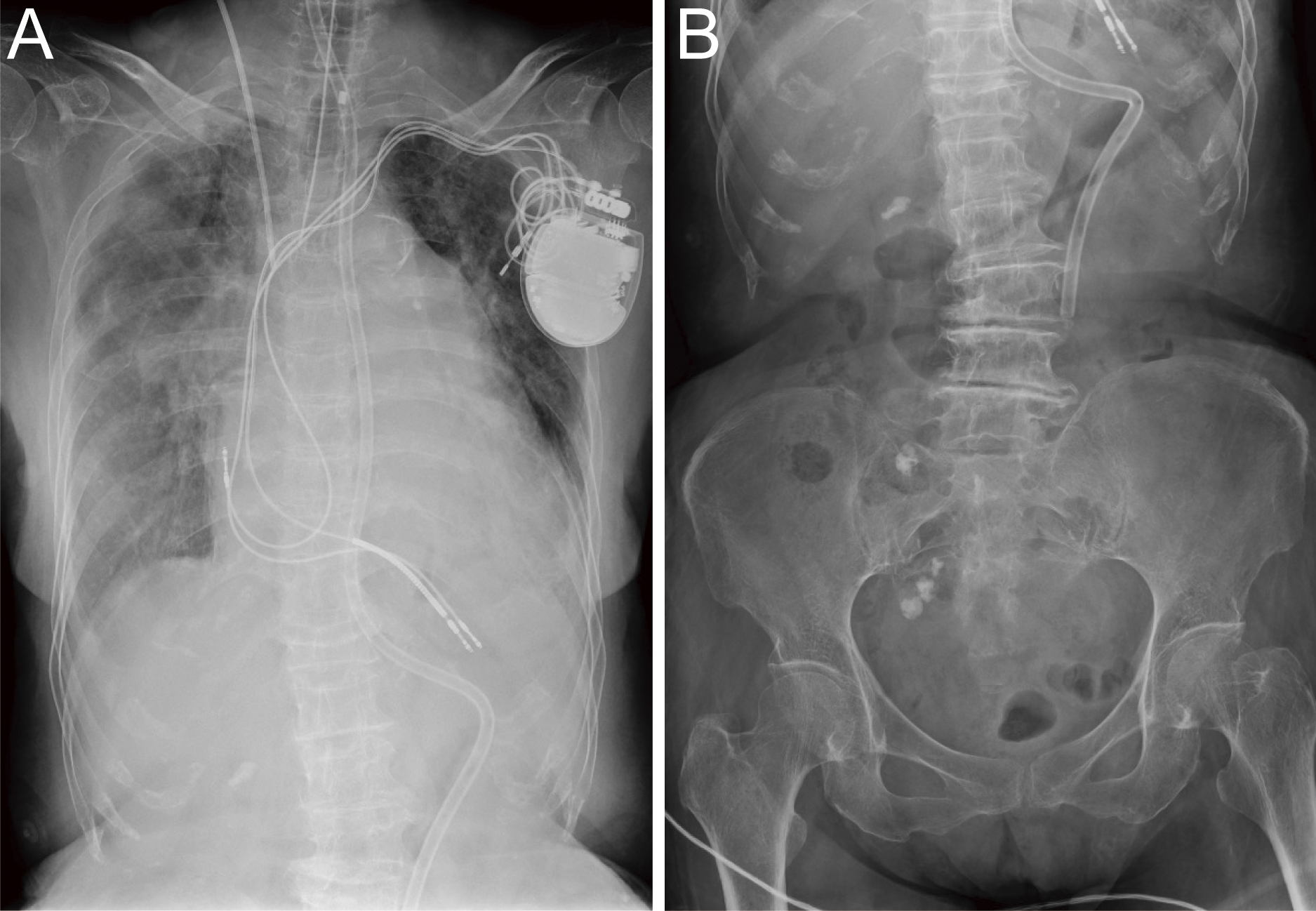
Figure 3. A: Gastrointestinal radiography using a nasogastric tube. The nasogastric tube tip (arrows) is positioned at the gastric pylorus, whereas the duodenum is immediately in contrast. The tube tip position progressed from the initial position, presumably via peristalsis. B: The nasogastric tube tip (arrows) was pulled back into the gastric body. The tube was adjusted and fixed in the nasal cavity at 55 cm.
From: Hypotensive Dumping Syndrome in Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy