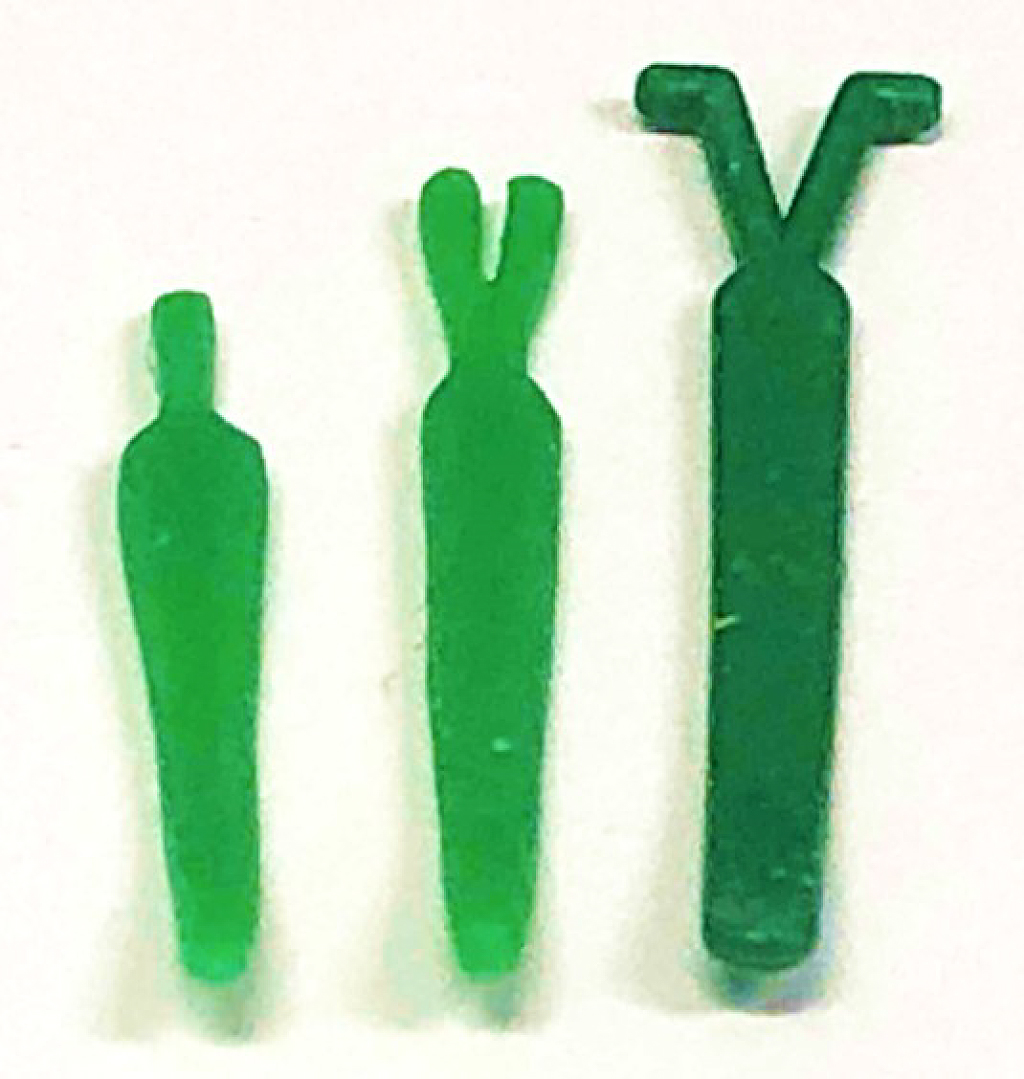
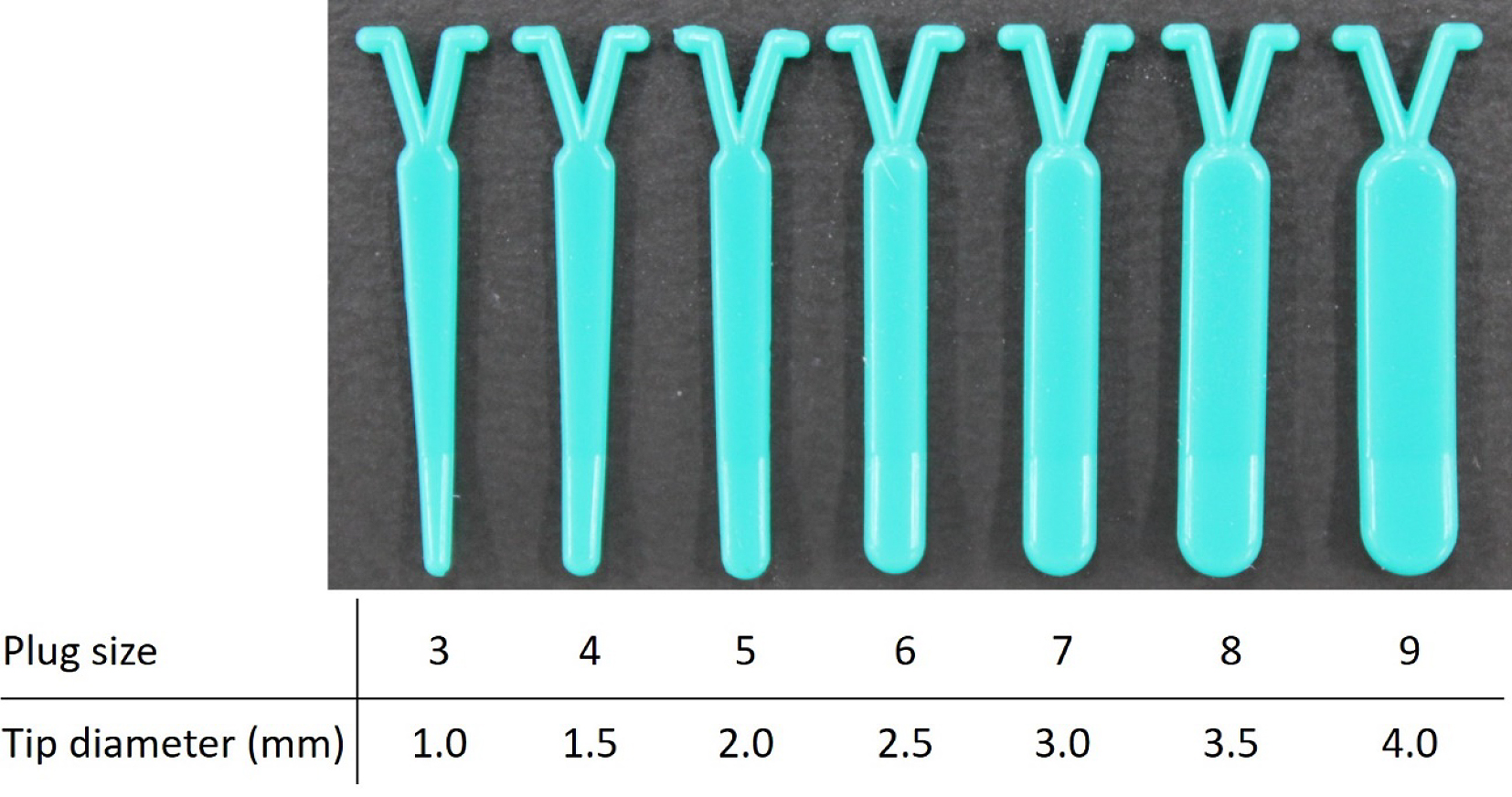
Figure 1. Surgical interventions classified by the procedure type: 1) tympanic membrane (TM) manipulation, 2) Eustachian tube (ET) injection, 3) plug surgery, 4) shim surgery, 5) tuboplasty, and 6) ET closure.
From: Management of Patulous Eustachian Tube
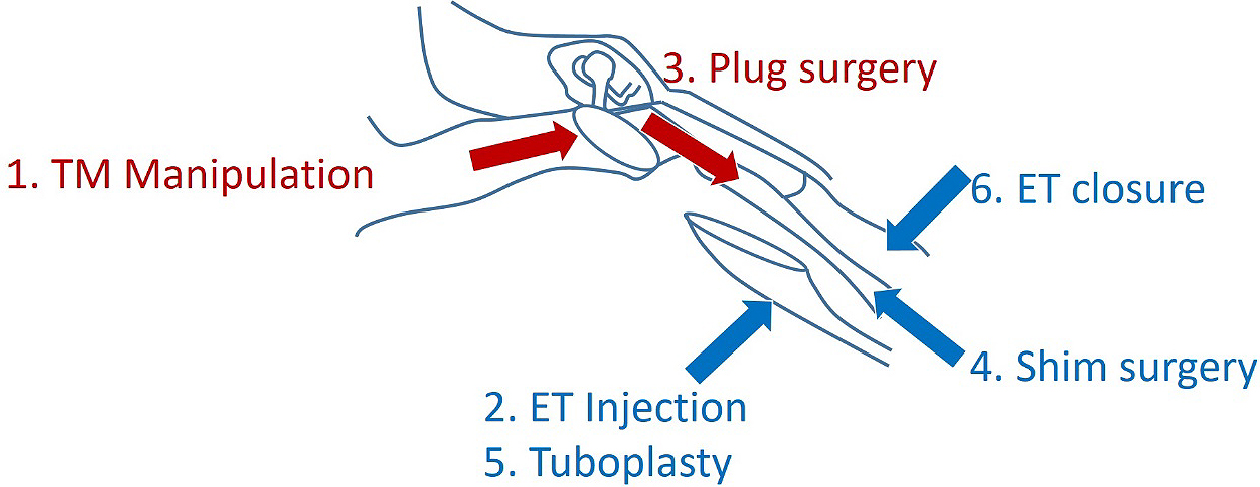
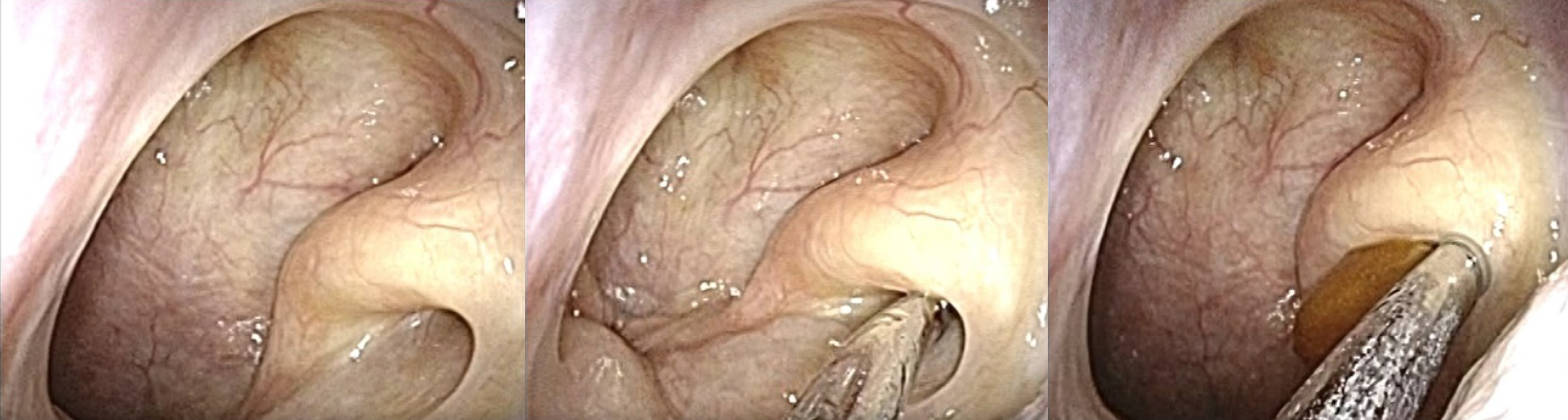
Figure 5. Endoscopic findings of the Eustachian tube’s bony portion (left peritubal cells (PTC) poor, middle PTC good with prominence, and right PTC good without prominence). White arrow; Eustachian tube, black arrow; prominence, and asterisk; peritubal air cell.
From: Management of Patulous Eustachian Tube
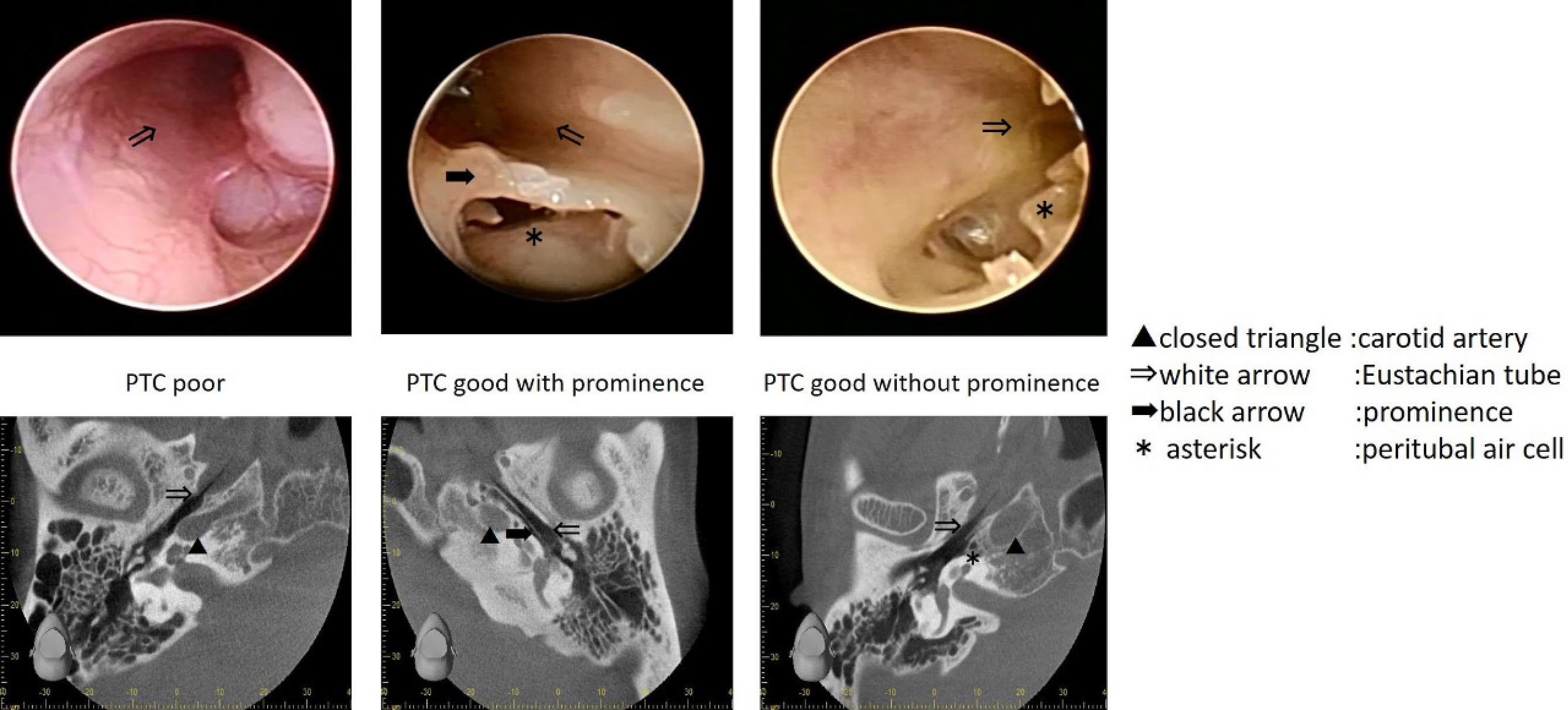
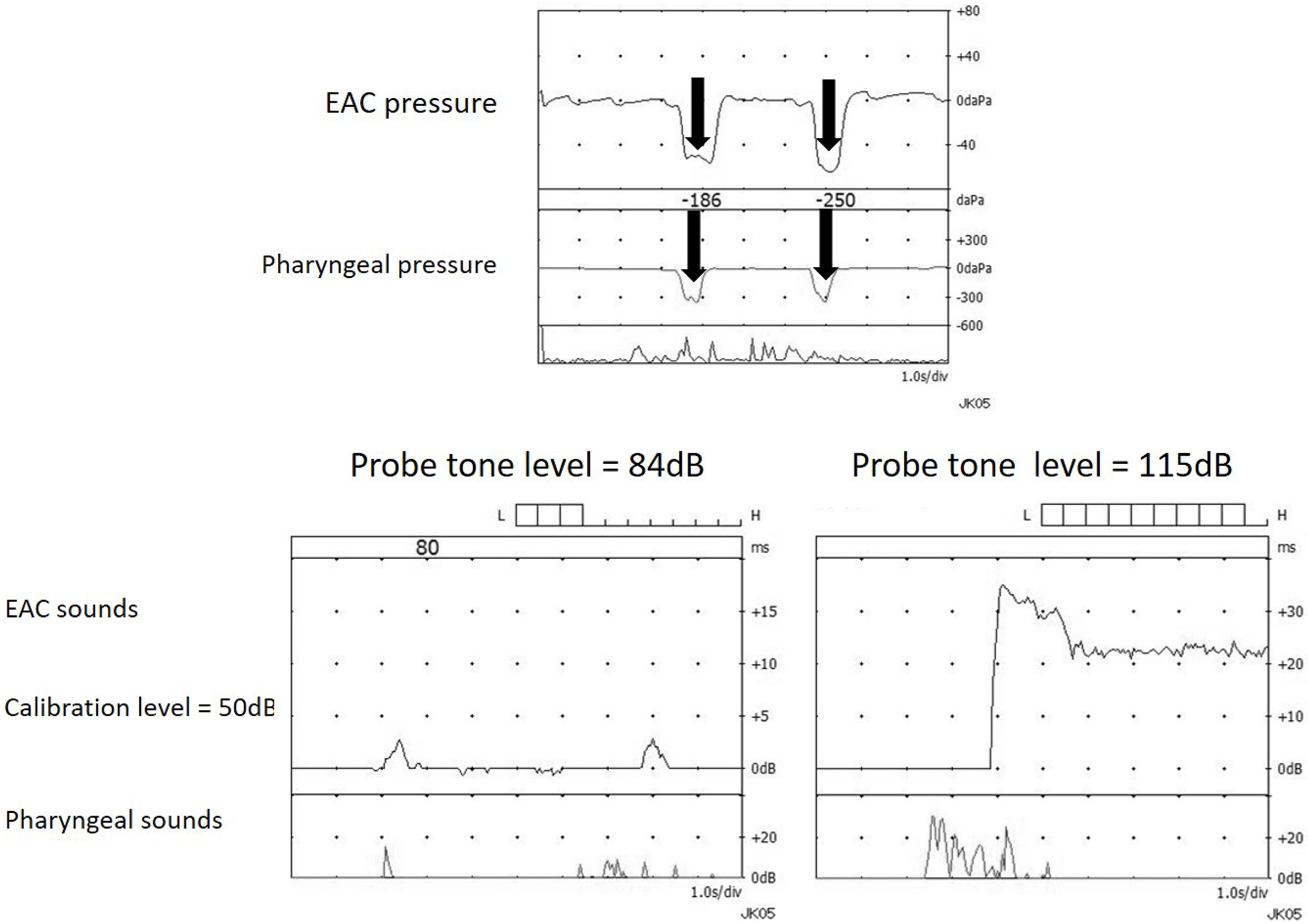
Figure 6. Typical tubo-tympano-aerodynamic graphy (TTAG) recordings in a Patulous Eustachian tube (PET) case (upper). In PET, synchronous changes in the external auditory canal (EAC) pressure are induced by respiration. Examples of typical sonotubometric recordings in PET cases (lower left and right). Lowering the probe tone SPL to less than 100dB (left). The ET opens when swallowing and remains continuously open thereafter (right).
From: Management of Patulous Eustachian Tube