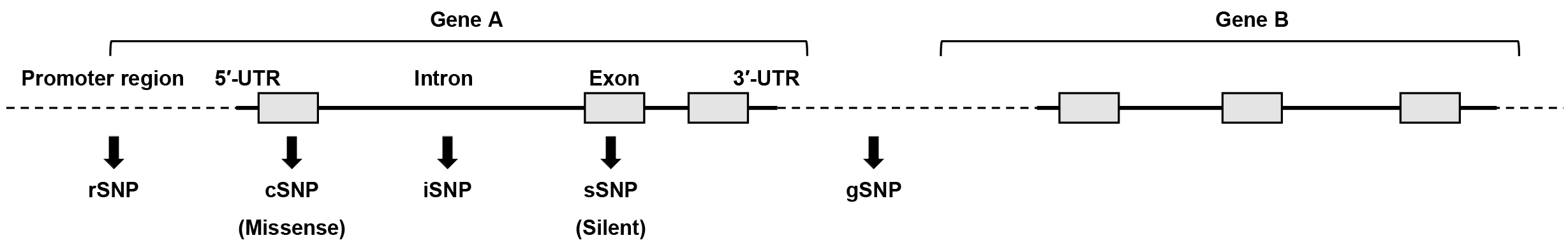
Figure 2. Gene function of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with therapeutic effects and adverse events of drug therapy. Underlined organs and treatments in parentheses mean target organ and treatment in which the gene function of SNPs is involved, respectively. ADT, androgen-deprivation therapy; ARPI, androgen receptor-pathway inhibitor.
From: Genetic Polymorphisms and Pharmacotherapy for Prostate Cancer
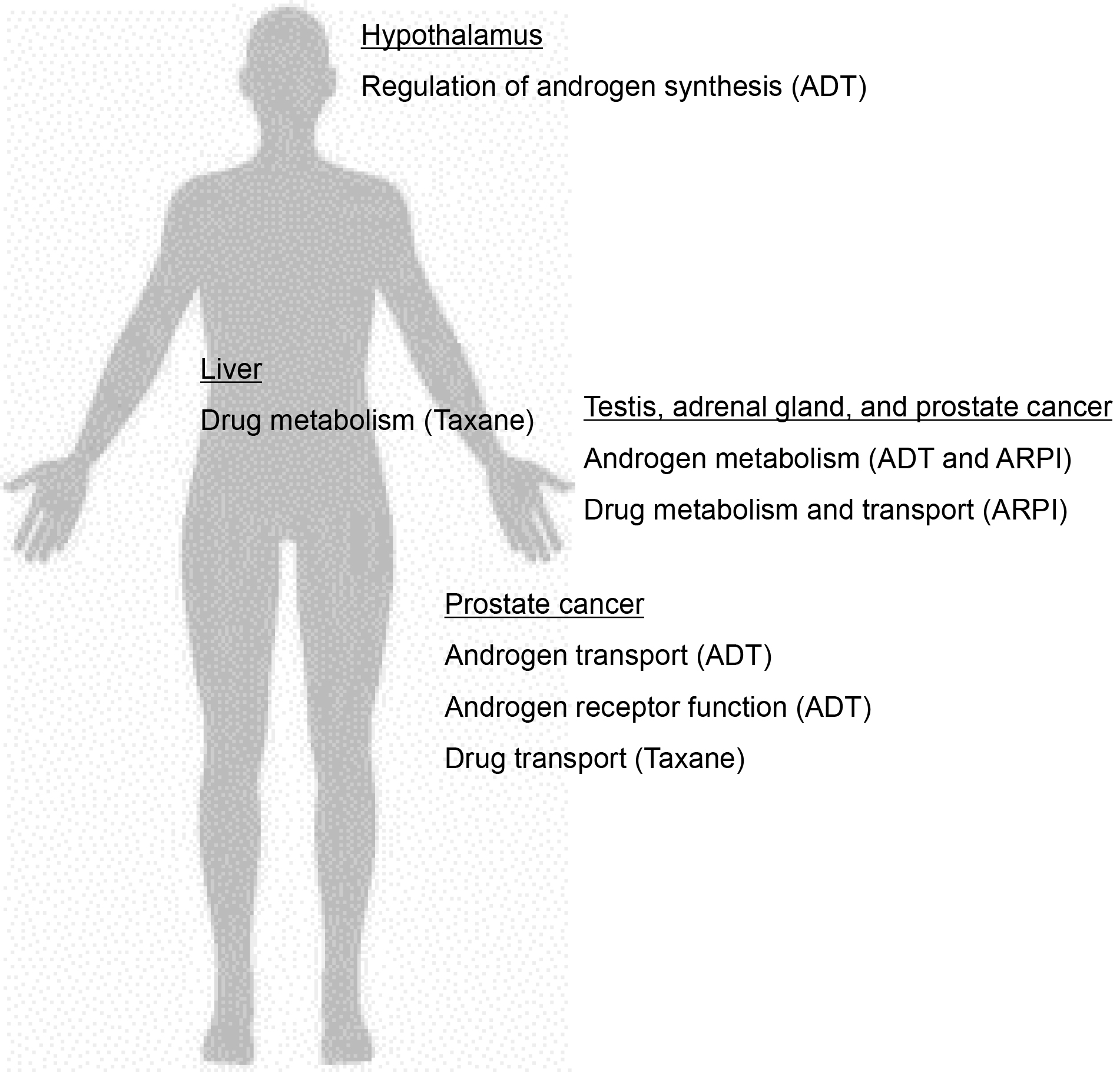
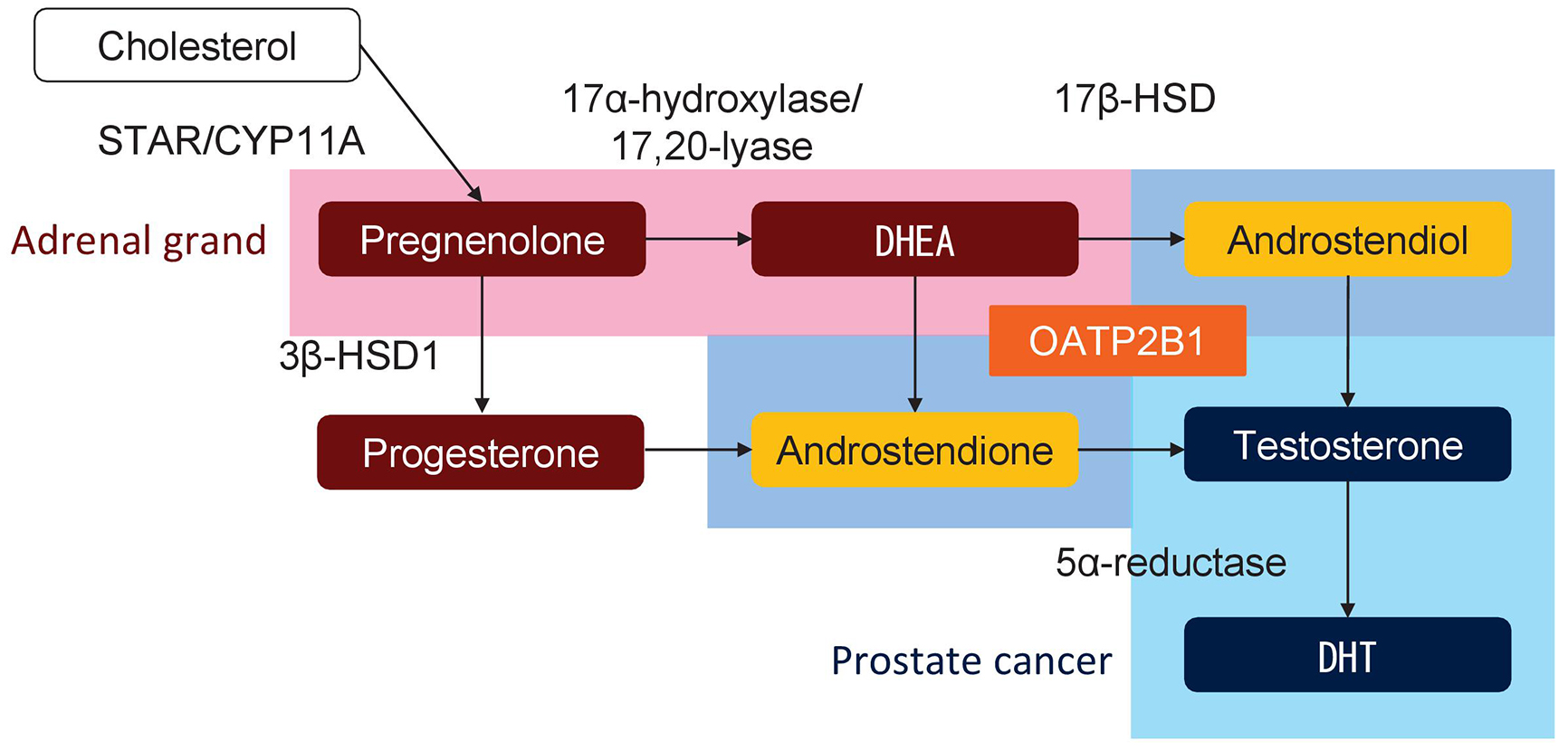
Figure 3. Schematic of molecules involved in androgen synthesis and uptake. The metabolisms surrounded by red, light blue, and blue are mainly processed in adrenal glands, prostate cancer, and both, respectively. OATP2B1 uptakes DHEA into prostate cancer cells. DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone; DHT, dihydrotestosterone.
From: Genetic Polymorphisms and Pharmacotherapy for Prostate Cancer